We often associate Gothic style with horror, the supernatural, and decadence, but this is actually a major misconception. Gothic style originated in architecture and can be considered an early precursor to the Renaissance in Northern Europe, long before Italy’s Renaissance. In art history, it stands out as one of the most brilliant gems.
Gothic Architecture
- The defining characteristics of Gothic style are grandeur and magnificence, while horror and the supernatural are later misinterpretations. Gothic literature and Gothic music arose after people saw Gothic architecture and were captivated by its appearance, mistakenly believing that these darker elements defined the Gothic style.
- The development of the Gothic style was motivated by the need to address the issue of flammable wooden roofs. In 1066, after the Norman Duke conquered England and became its king, the Norman dynasty began. This era saw a massive construction of churches, and to resolve the issue of traditional wooden roofs prone to catching fire, new architectural techniques were urgently needed.
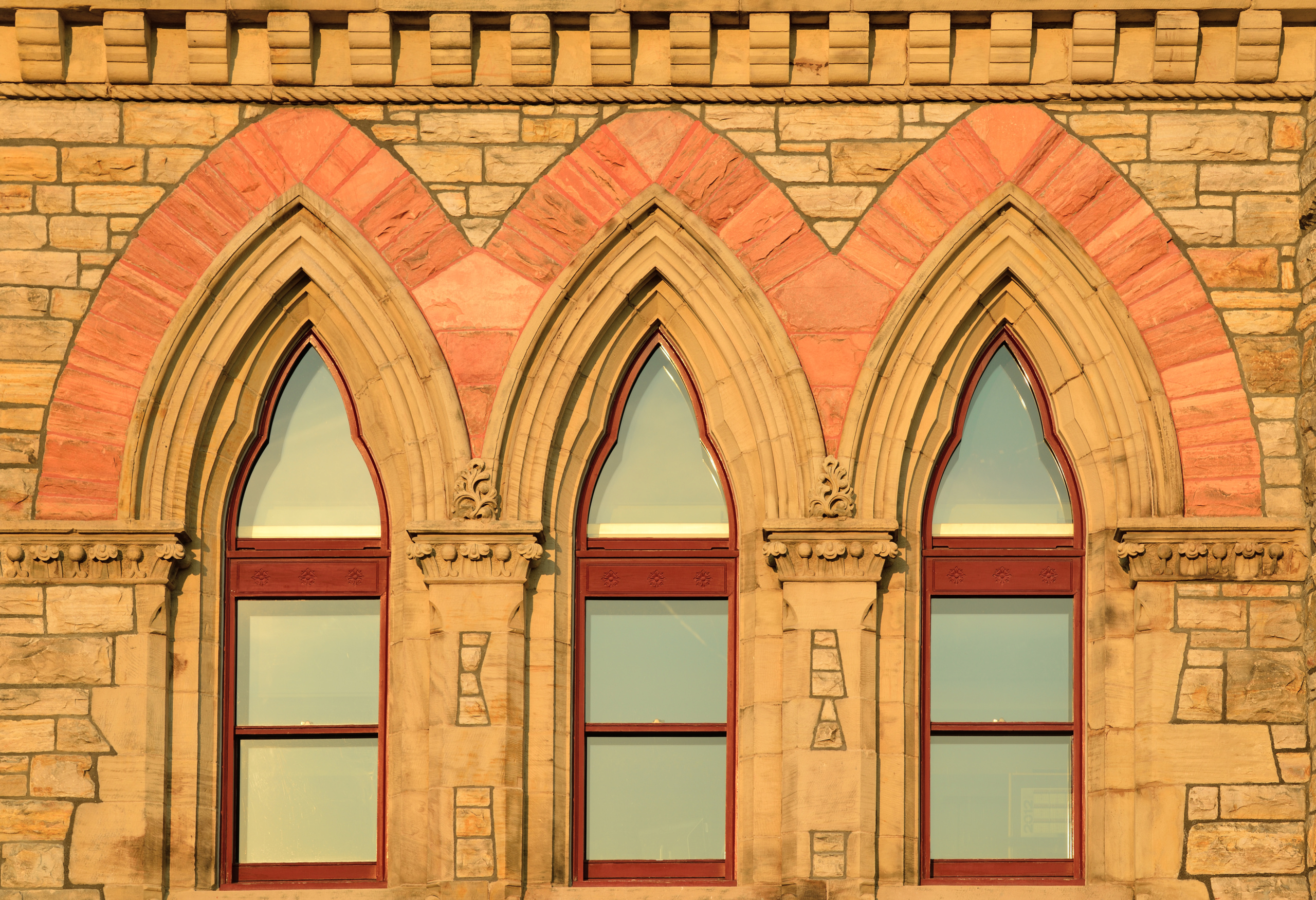
- The precursor to Gothic architecture was Norman architecture. In the Middle Ages around the year 1000, the ancient Roman dome-building technique had been lost. Architects at the time devised a solution using beams to create a framework, known as ribbed vaulting (Ribbed Vault, Fig. 1), and then filling the roof with lightweight materials (Figs. 2 and 3), thus solving the problem of wooden roofs. This style, known as Norman architecture, is also the precursor to Gothic architecture (Figs. 4 and 5).
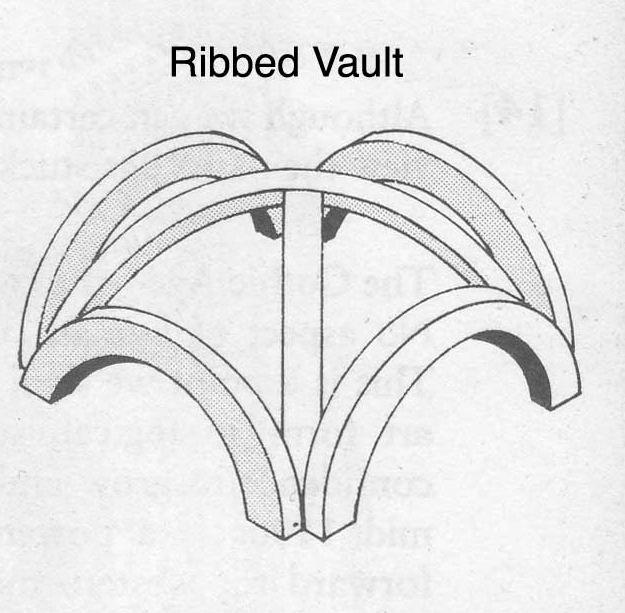
- (Figure 1) Rib Arch
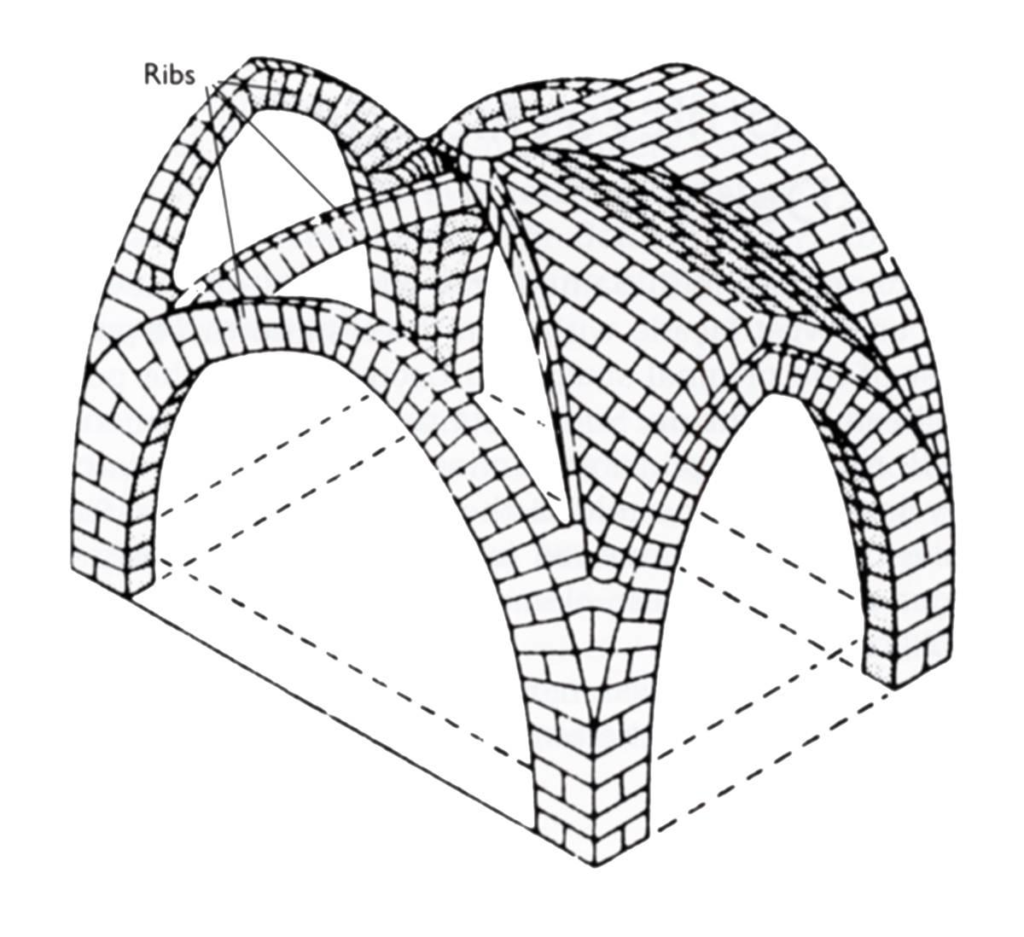
- (Figure 2) Filled with Lightweight Material
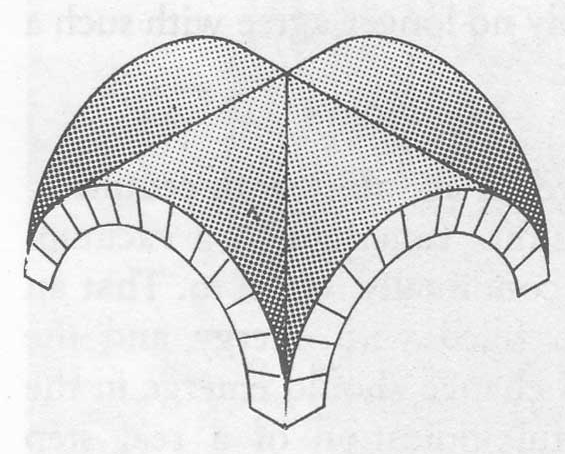
- (Figure 3) Filled with Lightweight Material
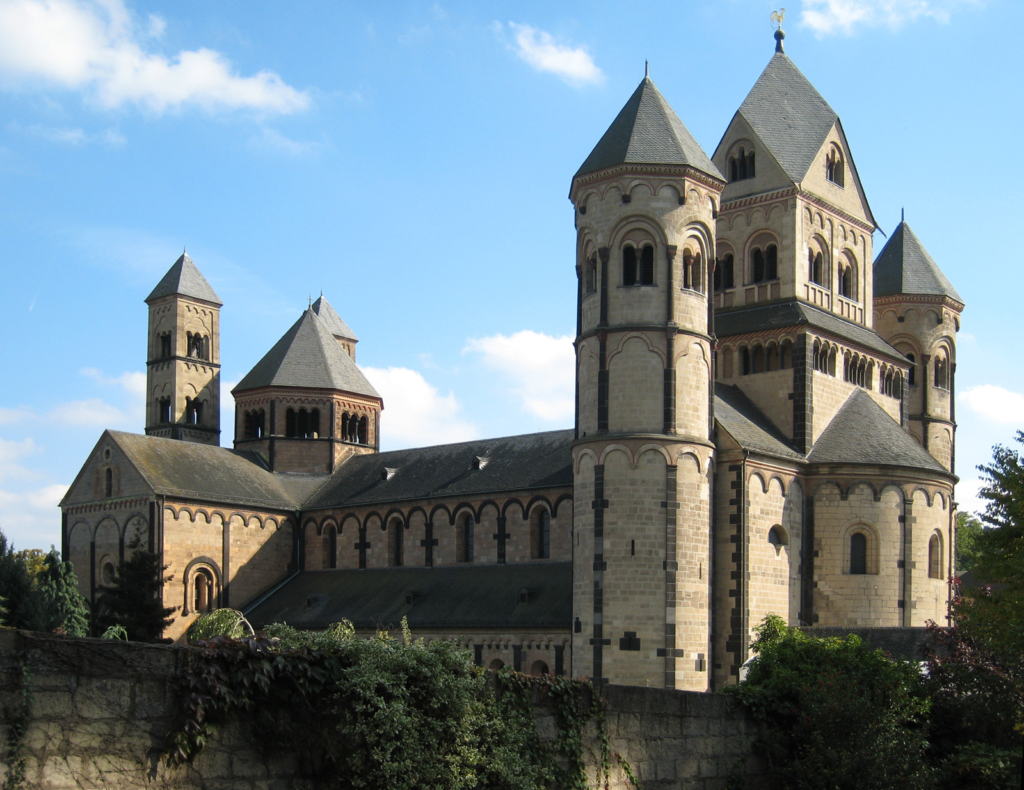

- (Figure 4) Representative Architecture of Norman Style
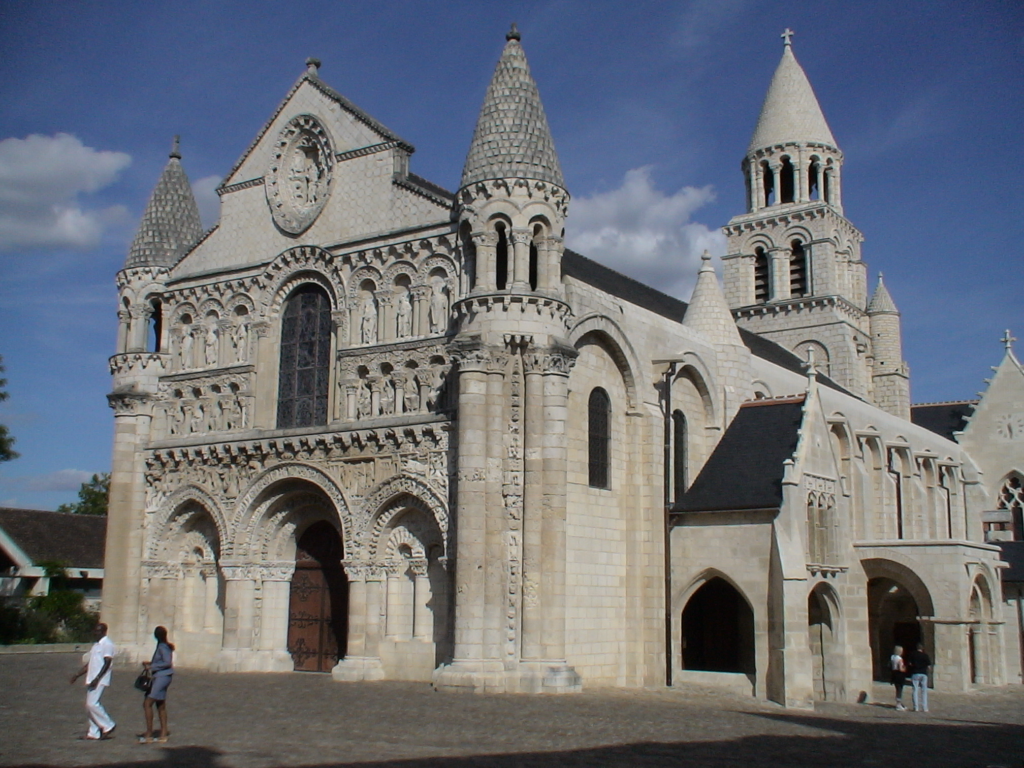

- (Figure 5) Representative Architecture of Norman Style
- Gothic architecture applies the concept of “first constructing a framework with ribbed columns and then filling it with lightweight materials” to the entire building, including the walls, which are also built using this method, resulting in Gothic structures. The walls of Gothic architecture are not filled with stone but instead replaced by large glass panels.
- The architectural philosophy of Gothic architecture reflects the core ideas of modern architecture. The fundamental concept of buildings prior to the Gothic style was stacking bricks from low to high. In contrast, the Gothic approach involves first constructing a skeleton and then adding the “flesh.” Similarly, modern architecture often starts with a steel framework before filling it with concrete, and even skyscrapers are entirely covered with glass on the exterior.
- Characteristics of Gothic architecture include pointed arches, flying buttresses, and internal ribbed vaults (Figures 7 and 8). The taller and sharper the spire, the closer it is believed to reach God (Figure 6). Flying buttresses extend from the exterior of the church like many arms, supporting the decorative arches above (Figures 9 and 10).

- (Figure 6) Cologne Cathedral
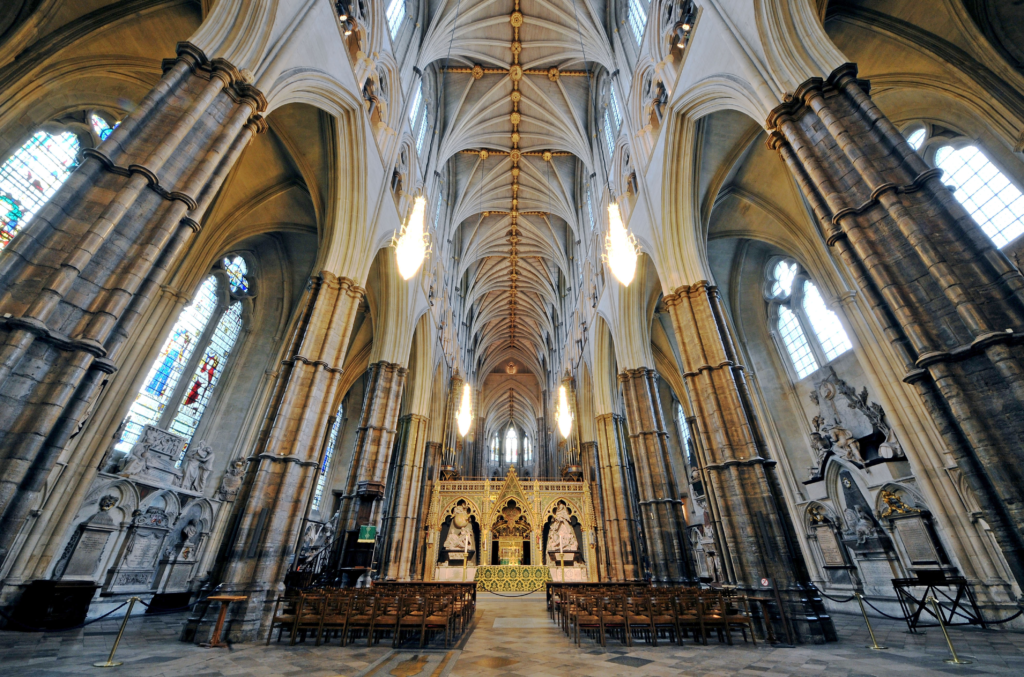

- (Figure 7) Westminster Abbey
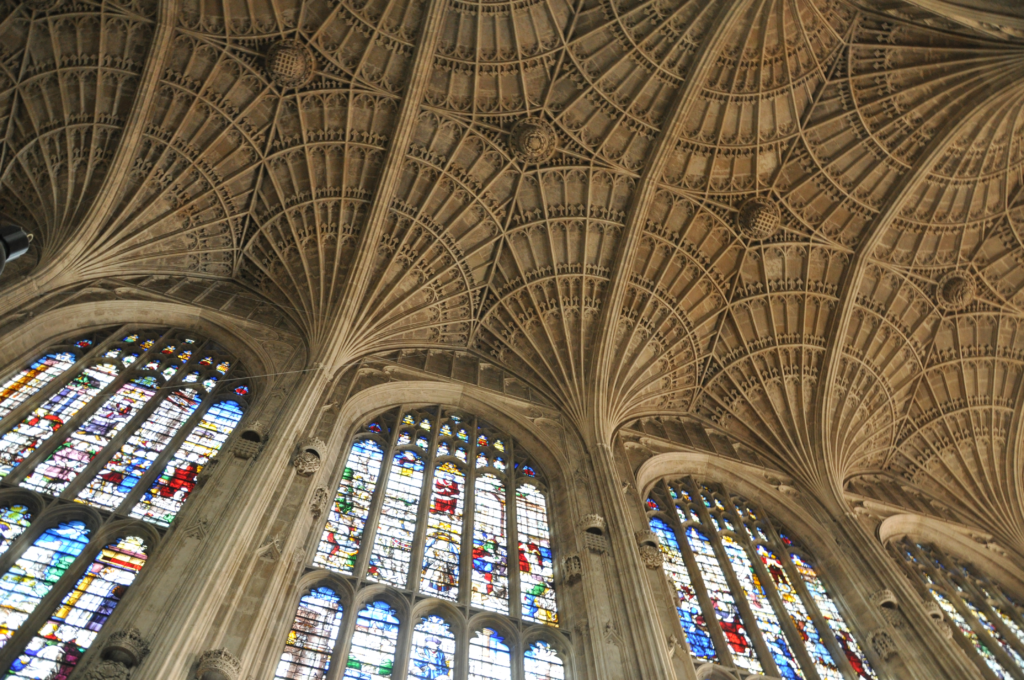

- (Figure 8) King’s College Chapel, University of Cambridge
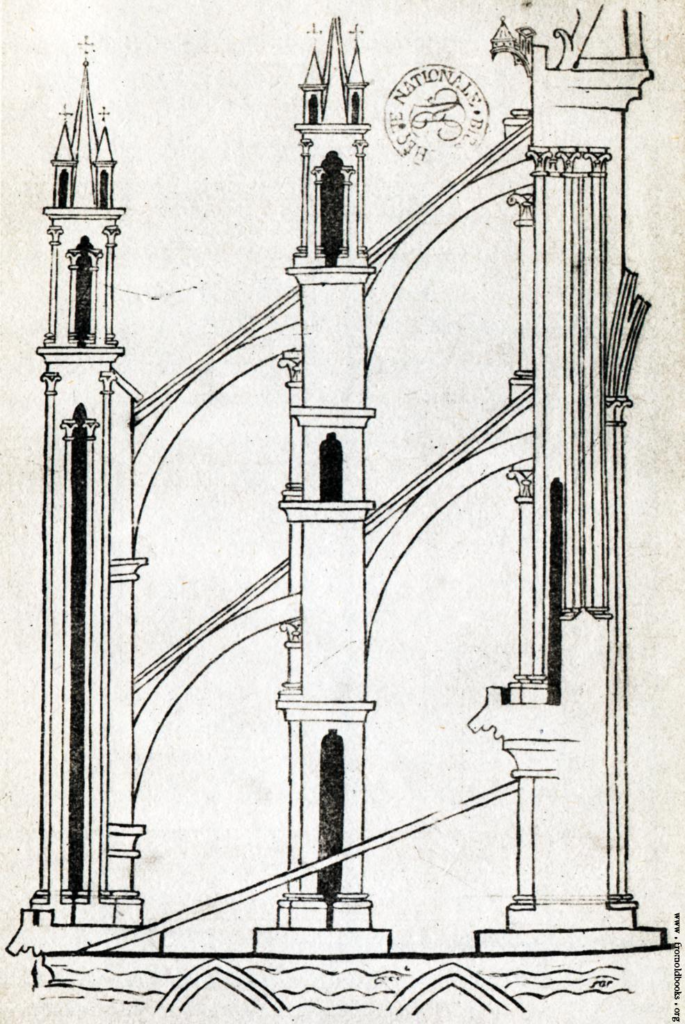
- (Figure 9) Flying Buttress
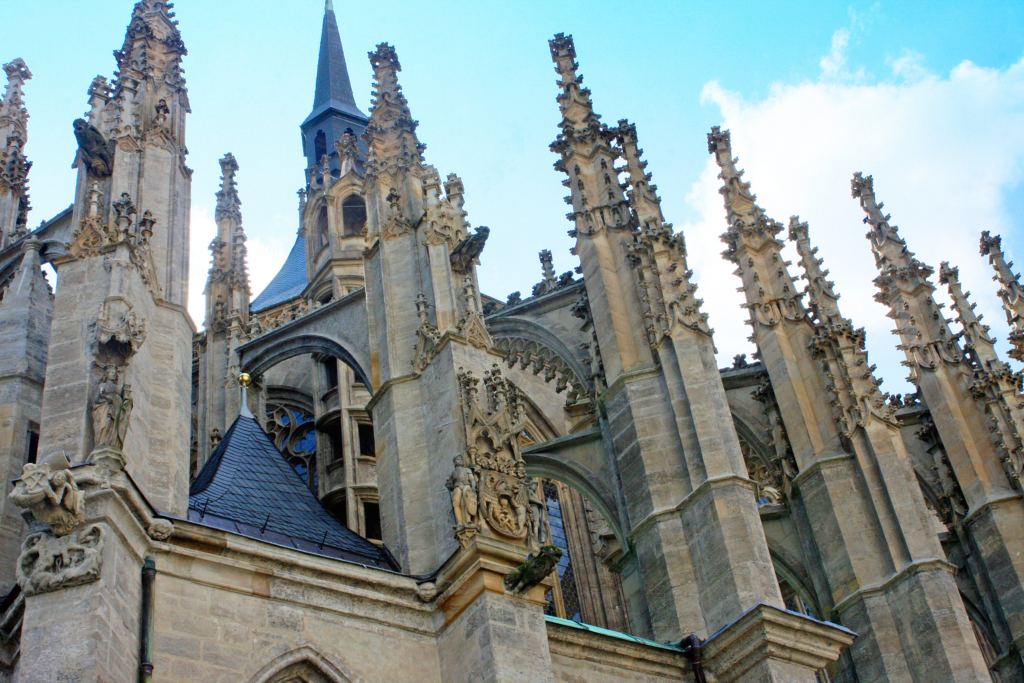

- (Figure 10)
- Gothic architecture can withstand significant pressure. Many Gothic cathedrals have increasingly taller spires, creating a hedgehog-like visual effect, aimed at aesthetically drawing closer to God, as seen in the Milan Cathedral (Figure 11).
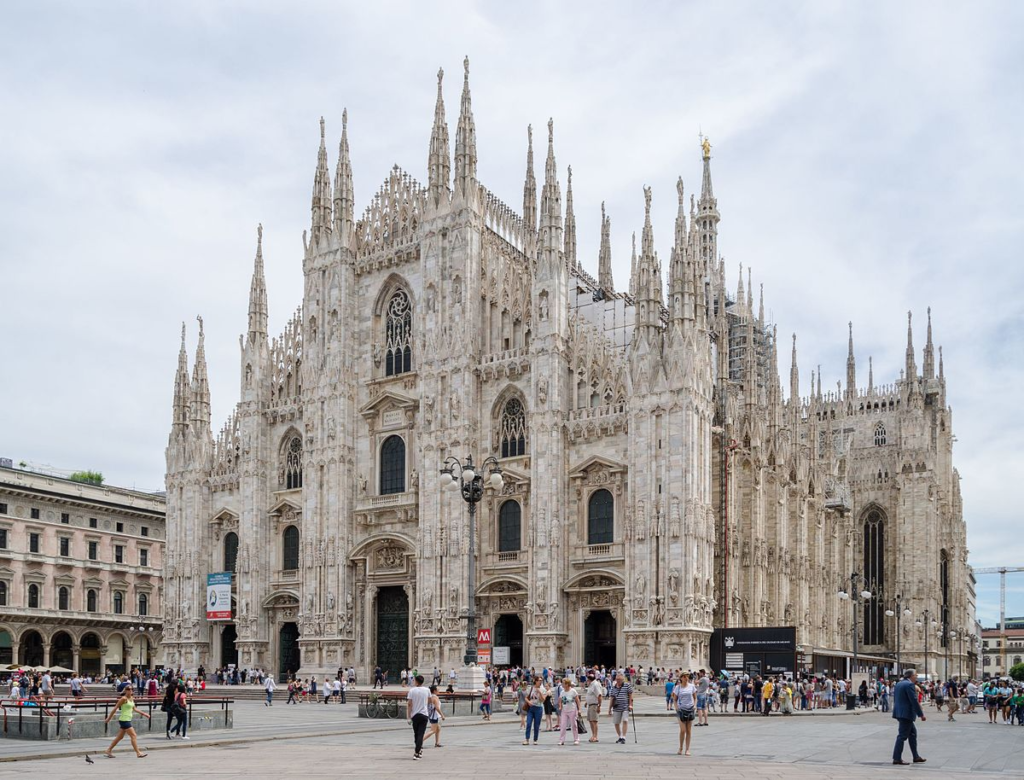

- (Figure 11) Milan Cathedral

- (Figure 12) Reclining Skeleton

- (Figure 13) Cartoon Skeleton Image
- The exterior of Gothic architecture features tall spires, thin walls, and large windows. This is in stark contrast to Romanesque architecture, which is characterized by large domes, thick walls, and small windows.
- Gothic churches convey a religious message that is entirely opposite to that of ancient Roman churches. Ancient Roman churches are very solid and evoke a sense of conservatism and strength. In contrast, Gothic churches are light and airy, with vibrant interiors and a sense of transparency that resembles the heavenly scenes depicted in the Bible, conveying a feeling of compassion and love.
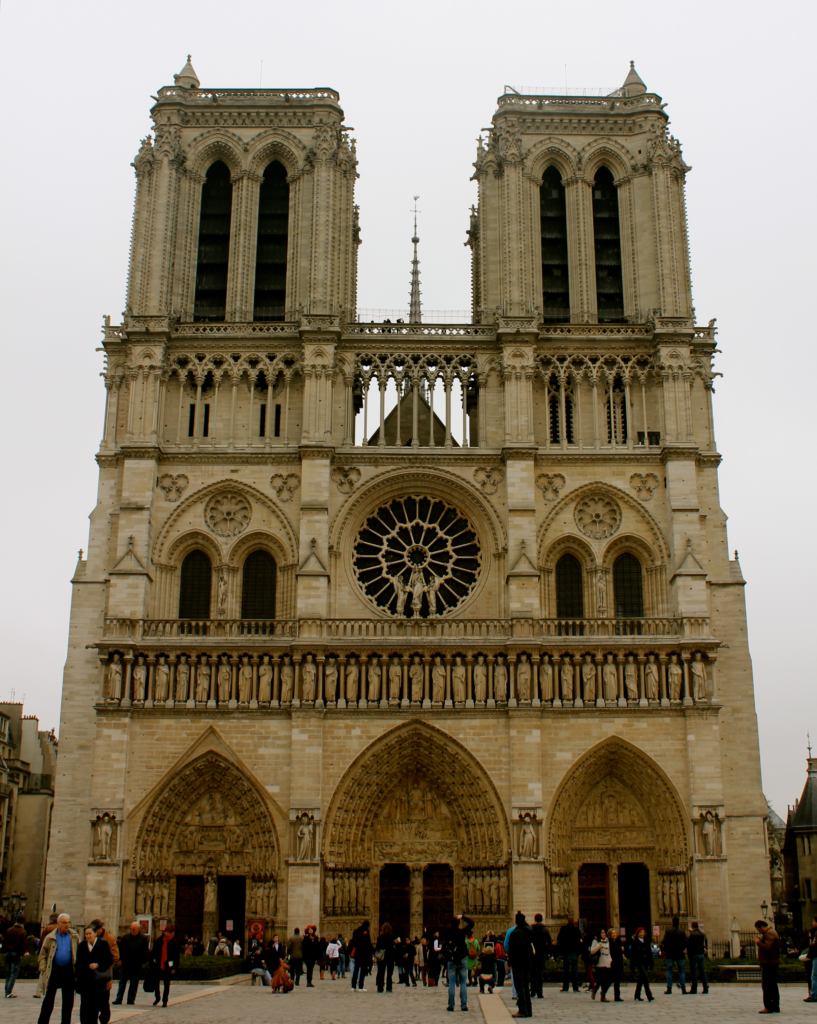

- (Figure 14) Notre-Dame Cathedral
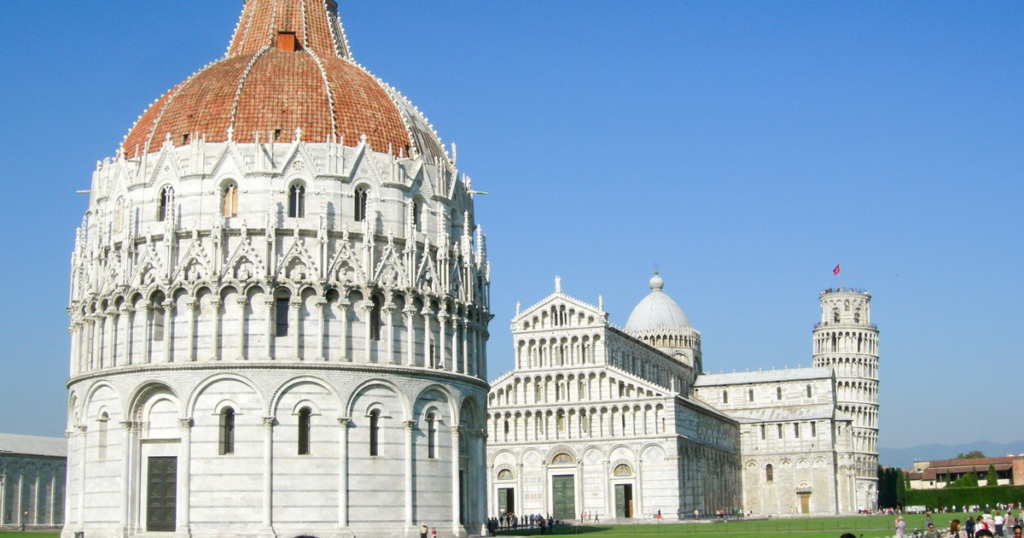

- (Figure 15) Romanesque Church of Pisa
Gothic Architecture Representative: Notre-Dame CathedralNotre-Dame
Cathedral is a prime example of Gothic architecture, and the familiar view of it features its pointed towers seen from the front.However, if you visit Notre-Dame Cathedral, be sure to first walk around to the back; the design of its nave is quite different from that of the main entrance. Additionally, there are often long lines to enter Notre-Dame, and the stairs are narrow. If you are uncomfortable in cramped spaces or suffer from claustrophobia, it is advisable to proceed with caution when entering.


